6 A&S Physicists Awarded Breakthrough Prize
Our universe is dominated by matter and contains hardly any antimatter, a notion which still perplexes top scientists researching at CERN’s Large Hadron Collider. The Big Bang created equal amounts of matter and antimatter, but now nearly everything—solid, liquid, gas or plasma—is…



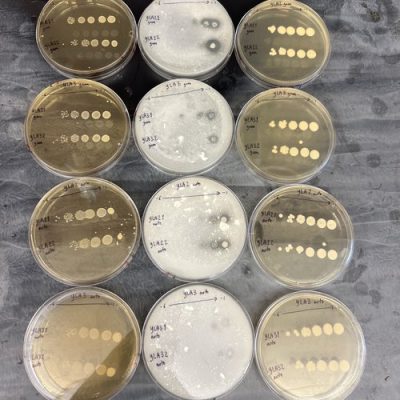
 “We aim to learn how microbiomes reassemble when they mix,” Oliverio says. “We want to see how mixing events impact the function of microbiomes and how often new communities with novel functions form.”
“We aim to learn how microbiomes reassemble when they mix,” Oliverio says. “We want to see how mixing events impact the function of microbiomes and how often new communities with novel functions form.”