Boasting an impressive wingspan of over seven feet, the golden eagle is one of the largest birds of prey in North America. In addition to being cunning, skilled hunters and their ability to soar effortlessly for hours, golden eagles might also utilize strong gusts of wind to assist their flight – an ability that piqued the interest of Kasey Laurent, an aerospace and mechanical engineering professor in the College of Engineering and Computer Science.
During her Ph.D. studies at Cornell University, Laurent conducted research on golden eagles by recording their acceleration as they flew, and the study formed the foundation for her dissertation on bird and drone flight. She also participated in Cornell’s Raptor Program, which provides a home for injured or non-releasable birds for research, training and rehabilitation. This experience gave her valuable insights into bird flight and behavior.
“Slowly throughout my Ph.D., I became more of a bird person. That’s what motivates my research here at Syracuse University,” Lauren says.
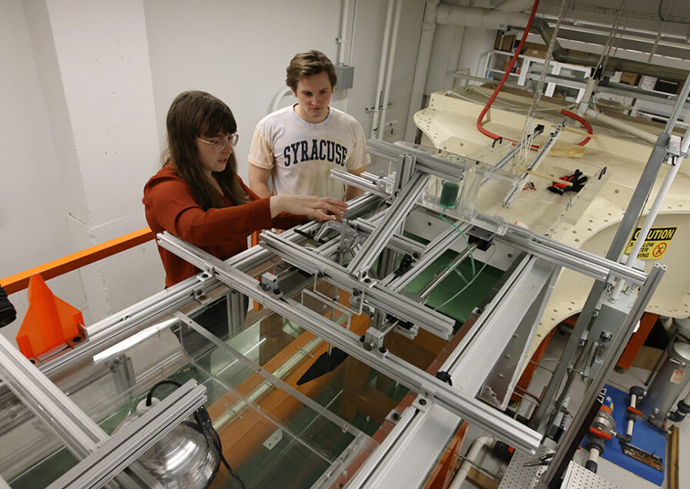
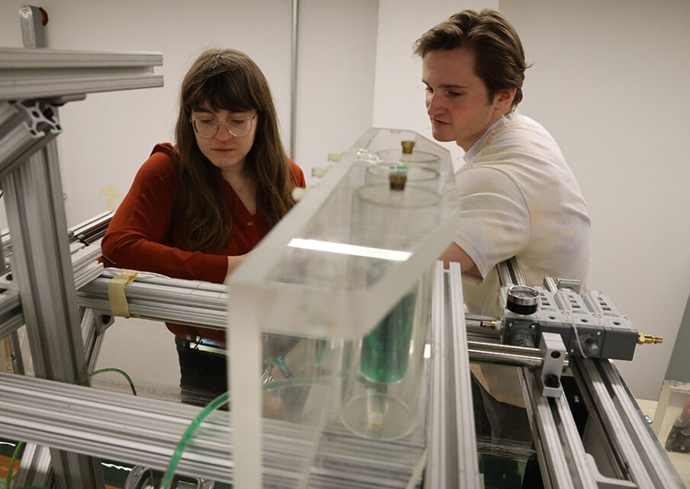
Laurent’s research aims to enhance flight and aerodynamics by measuring wind speeds and unsteadiness within air flows. Her work’s interdisciplinary nature also enables collaboration with biologists to explore ideas for improving aerodynamics by learning from nature.
“If you step outside on a windy day, you’ll feel the wind coming from various directions and at varying strengths at random intervals,” says Laurent. “If we measure the wind at a single point in time, that value will be random, but if we measure the wind over a long period of time and evaluate the statistics of how the wind changes over time, we’ll find patterns. My research looks at how these patterns, or signatures, may be deduced by looking at the locomotion of animals in turbulent environments. Will a bird fly a certain way in the turbulent atmosphere?”

As Laurent puts together a proposal for gust soaring seen with golden eagles, she’s also interested in gathering data from crows, goshawks, and turkey vultures, large birds that also use strong wind gusts to aid their flight.
“Goshawks fly through the forest and can maneuver very fast in different environments. When flying close to treetops, turkey vultures’ wings have an angle to them, allowing them to restabilize. It would be difficult to replicate this in man-made vehicles since they’re not flexible and don’t have joints like birds, but there’s still much we can learn.”
Studying how birds utilize wind and atmosphere to aid their flight would assist in improving the flight of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs.) Smaller aircraft often face issues when encountering wind gusts, causing them to lose control and potentially crash. Understanding how to maneuver around gusts could open up new possibilities for aircraft to fly in without sustaining damage from wind gusts and even utilize gusts to their advantage, similar to birds.
This research can be useful in creating smaller and lighter UAVs for various applications, including search and rescue missions. The main challenge with drones is that they have a limited range, which requires them to return to a base to change batteries and repeat the process. If the drones have a longer lifespan, they can continue with their search without the need to land or replace the battery.
“If we find a way to let the gusts move aircraft around, power won’t be an issue. We’ll just need to know how to maintain stability in that gust,” Laurent says. “Most research looking at flight in turbulence aims to develop methods to reject gusts, but it seems, according to the eagles, that may not be the best approach. We can learn a lot from nature to improve aerodynamics and locomotion.”