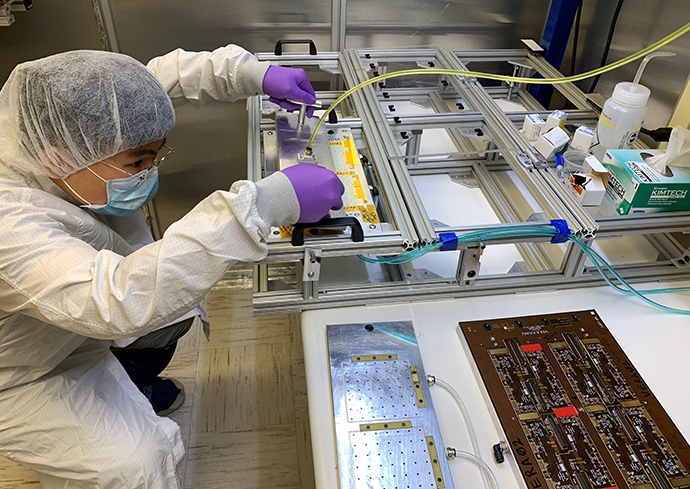
College of Arts and Sciences (A&S) physicists just launched a new tracking device to research the fundamental forces and particles in the universe. The device, known as the Upstream Tracker, was installed at the renowned European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) laboratory on the Swiss-French border just outside of Geneva, which uses some of the world’s largest and most complex scientific instruments to study fundamental particles.
The Upstream Tracker is part of an ambitious upgrade to the “Large Hadron Collider beauty (LHCb)” experiment taking data at the Large Hadron Collider at CERN, which aims to uncover information about the universe through science known as new physics. New physics is knowledge that enhances the current understanding of how the universe works. The university’s High-Energy Physics group working at LHCb led an international team of collaborators that designed and constructed this detector.
The installation is the culmination of a decade of research and work, led by physics professor Marina Artuso. The project received nearly $7 million in awards from the National Science Foundation, with a majority of the funds going directly to Syracuse research.
The Upstream Tracker will help scientists search for knowledge beyond the “Standard Model” of physics, which is the current best theory about the building blocks of the universe. The Upstream Tracker is a crucial component of the LHCb tracking system, used to reconstruct the positions of the subatomic particles produced in the proton-proton collisions, and is part of a high-speed processor that implements sophisticated algorithms to make real-time decisions about what to record. It’s technology that will empower physicists to make key discoveries about fundamental particles.
While the Standard Model explains a great deal about the physical matter and forces in the universe, there are significant phenomena that it doesn’t explain, says Artuso, like the existence of dark matter and dark energy, which are invisible but account for about 95 percent of the universe, and the reason why the current universe is stable. The LHCb and Upstream Tracker were designed to help physicists solve these big mysteries through new physics.

Nearly 50 undergraduate students and tens of graduate students contributed to this project over the years and several Syracuse faculty members played key roles, including the late Sheldon Stone, who served as project deputy, along with physics professor Steven Blusk, who led test beam studies of detector prototypes, associate physics professor Matt Rudolph, who led the sensor acquisition, physics professor Tomasz Skwarnicki, who is leading the software effort to process the detector information. Physics research assistant professor Ray Mountain was a key player in the detector mechanics and oversaw the production of the detector units in the clean rooms built for this project.
“One of the main tenets of my physics work is to solve mysteries about how the universe works through new physics. But, new physics can be very subtle, elusive, and difficult to detect. Nature wants us to work a little harder to find these secrets. The Upstream Tracker is a key component of the upgraded LHCb detector that is poised to observe rare processes between particles that occur below the current sensitivity level,” says Artuso.
For the full Q&A with Artuso and a pair of alumni share their experience on this project and offered insights about what they hope this device will contribute to human knowledge, visit artsandaciences.syracuse.edu.
Story written by Emily Halnon.