Helping Ranchers Learn From the Wild
Tropical forests garner headlines as greenhouse gas storehouses. But wild grasslands are crucial, lesser-known candidates as climate heroes. Wild grasslands—from the African savanna to the North American prairie—have the potential to soak up vast amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
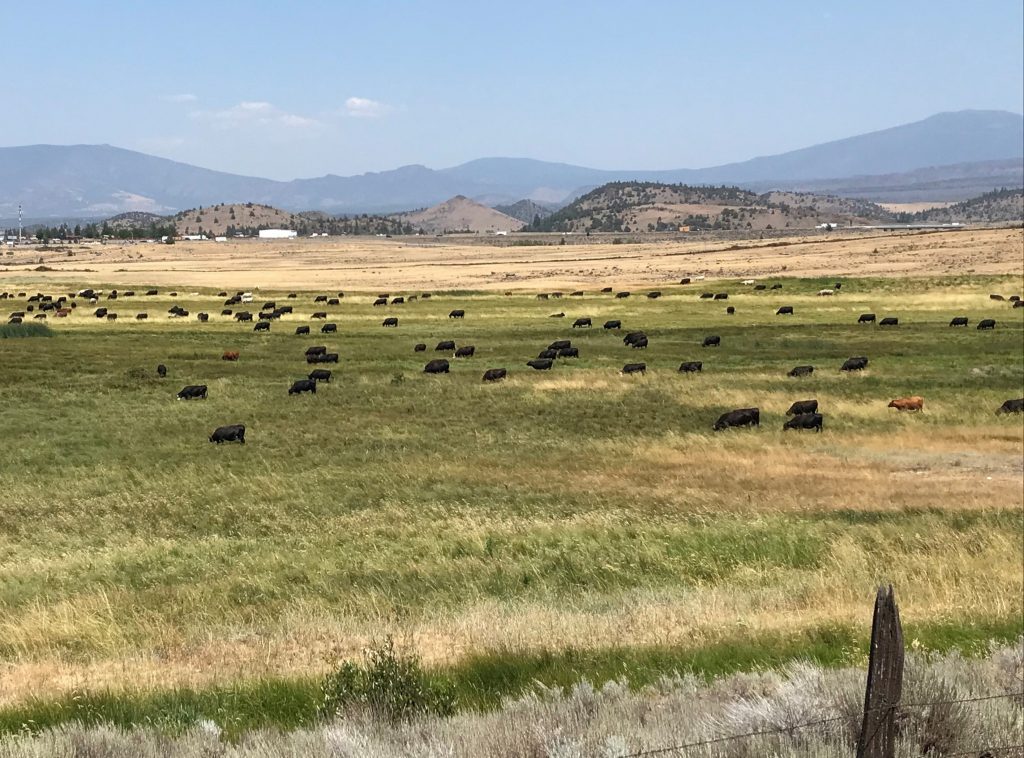

When migratory herds graze on grasses and shrubs and move on to new territory, plants respond by growing fresh shoots. This stimulated growth absorbs atmospheric carbon in plant leaves and roots, which eventually gets trapped in grassland soils, removing it—and its heat-trapping properties—from the atmosphere. For example, when vast bison herds migrated on the Great Plains, their grazing behaviors and grassland’s subsequent carbon storage helped maintain stable ecosystems and global climate.
Mark Ritchie, professor of biology in the College of Arts and Sciences, hopes more family- and tribal-run ranchers could capture additional carbon in their soils by learning from wild ecosystems. By doing so, ranchers could qualify for market certifications for climate-friendly or carbon-neutral beef that are similar to certifications for organic or antibiotic-free foods.
Large-scale beef production has come under criticism for high levels of greenhouse gas emissions. But improving specialized beef supply chains and markets for carbon-neutral beef—and innovative ranching practices—could start turning that around.

“Ranches could become more climate-friendly or carbon-neutral by adopting management practices that mimic some characteristics of wild grasslands,” says Ritchie.
For instance, ranchers could rotate high numbers of animals through multiple pastures and paddocks for just a few days each and then fatten them during the last feeding stage with a diet of hay and other grasses instead of corn.
Ritchie is collaborating with Sustainable Northwest, an organization based in Portland, Oregon, which recently announced receiving a $10 million grant award from the U.S. Department of Agriculture. The organization’s Regenerative Ranching program partners with Country Natural Beef, a cooperative of more than 100 family ranches that manage several million acres in the West.
The grant would support the nation’s largest climate-focused beef production program across nine western states. It would be among the first programs in the nation to develop, implement and measure how beef producers can sequester greenhouse gases in grassland soils.
Ritchie and his team plan to develop a computer model for ranchers based on a minimum of inputs that will use regional baseline data of soil type, soil carbon and plant life characteristics. Ranchers could plug in their location and other data about their property and determine their best course without requiring a soil test. The user-friendly model could encourage more underserved and marginal ranchers to participate in the program.
“Ranchers could see how their soil carbon would change depending on their region’s characteristics and their management choices,” says Ritchie. “The model would allow them to make predictions under different climates and soil types for how much carbon storage in soils should change based on their management choices. They could compare their current management practices to desired practices and decide what is the best fit for their situation.”
Story by John H. Tibbetts