Using the solutions observed in nature to address global challenges in health, medicine and materials innovation is at the heart of research by BioInspired Syracuse. Austin Garner, assistant professor of biology and member of BioInspired, specializes in functional morphology—studying the form and function of animals and then applying it to bio-inspired designs in a wide range of applications.
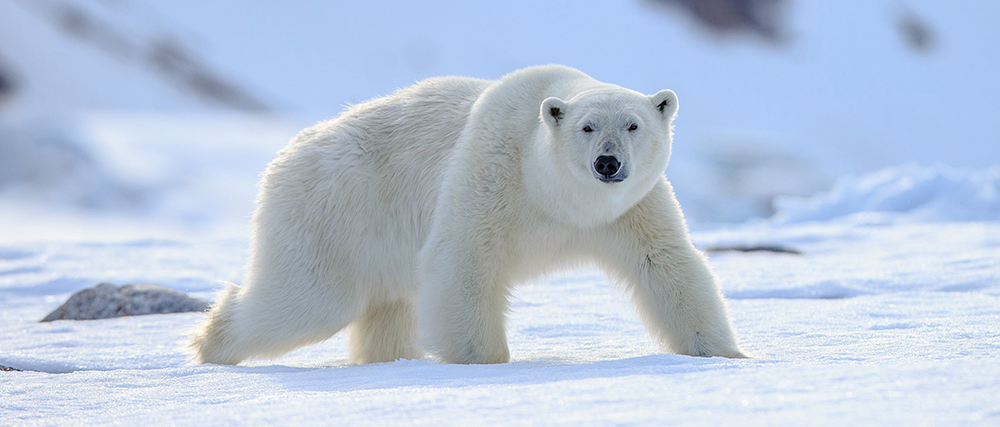
Garner recently co-authored a paper in the Journal of the Royal Society Interface exploring design principles on polar bear paws, which allow them to have better traction on ice compared to other bear species. The work identifies a new nature-based method that could be incorporated into human engineering challenges associated with traction, namely for products that slip on snow and ice such as tires and shoes.
Garner took part in the research as a Ph.D. student at the University of Akron. His collaborators were Ali Dhinojwala, the H.A. Morton Professor of Polymer Science in Akron’s School of Polymer Science and Polymer Engineering, and Nathaniel Orndorf, a 2022 Ph.D. graduate from Akron who now works as a senior material scientist at the tire company Bridgestone Americas.
They used actual samples and replicas of bear paw pads from museums, taxidermists and other collections, and imaged them using a scanning electron microscope and a surface profilometer, instruments that can measure surface texture and features. The team also created 3D printouts of the structures to vary diameter and height of features and tested them in the lab to see how they reacted to snow conditions.
The group specifically studied the hard bumps on the foot pads of bear paws called papillae, which have long been thought to help them grip ice and keep from slipping. The team discovered that the papillae on polar bears were taller than other species—up to 1.5 times. Importantly, the taller papillae of polar bears help to increase traction on snow relative to shorter ones.
Even though polar bears have smaller paw pads compared to the other species (likely because of greater fur coverage for heat conservation), the taller papillae of polar bears compensate for their smaller paw pads, giving them a 30-50% increase in frictional shear stress—or lateral grip.
“This is exciting interdisciplinary work that studied a long-held belief that the micro-structures on polar bear paw pads were an adaptation to increase traction on ice and snow,” says Garner. “Our work shows that the papillae themselves are not an adaptation for this because other bears have them, but the unique dimensions of polar bear papillae do confer an advantage in traction.”
The team now hopes that other scientists and manufacturers can apply their research to product design. For example, snow tires now have deeper treads than all-season tires, but this research could also suggest design modifications for increased traction.
Read the team’s full paper, “Polar bear paw pad surface roughness and its relevance to contact mechanics on snow,” in the Journal of the Royal Society Interface.